Europe's Drought Crisis: Is Desertification Our Future?
The intensive food industry is fueling a desertification crisis, transforming once lush forests into barren landscapes dominated by plastic and metal greenhouses. This shift has severe consequences for our environment, biodiversity, and economy.
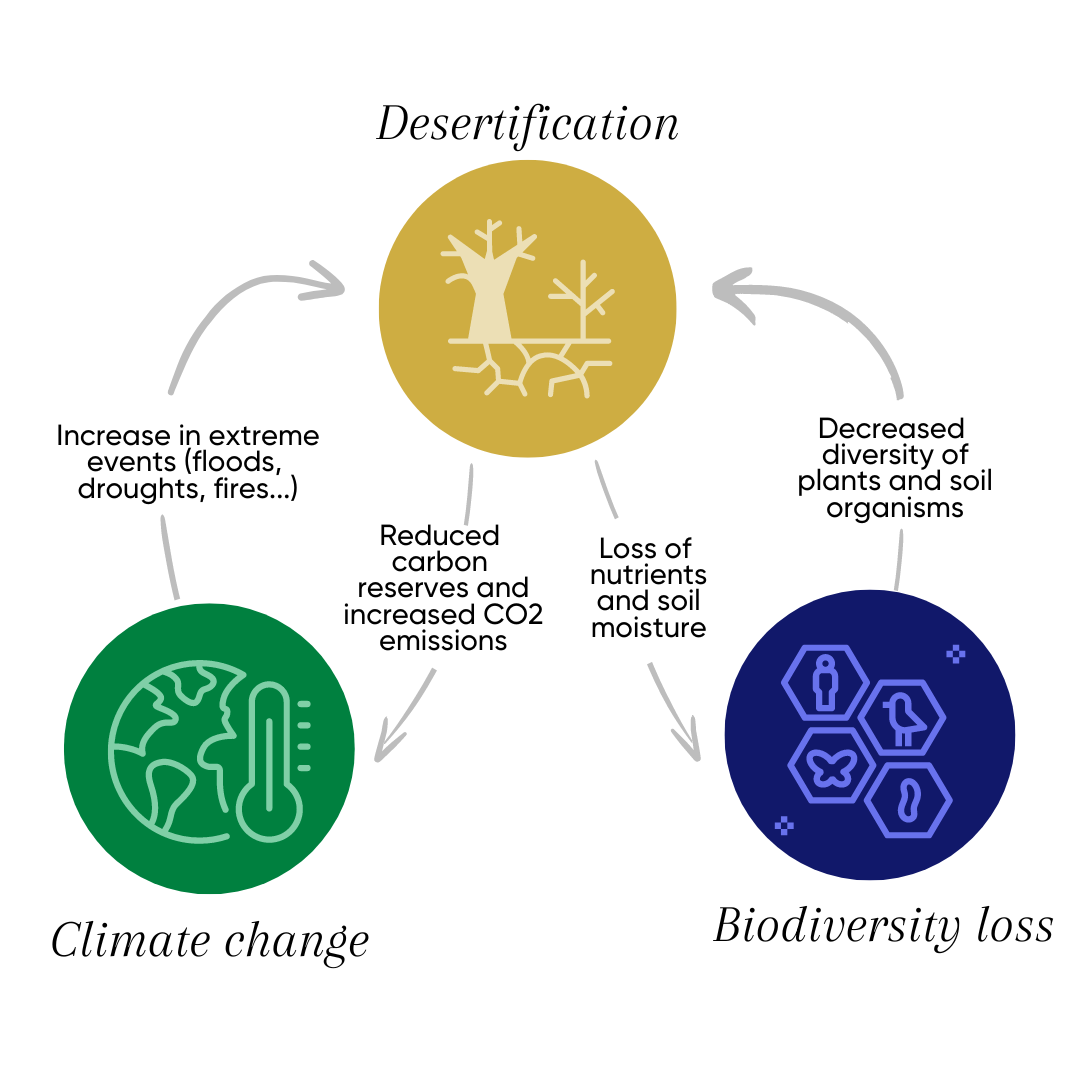
Desertification means: land degradation in arid, semi-arid, and dry sub-humid areas results from various factors, including climatic variations and human activities. Desertification can bring about poverty, health problems due to wind-blown dust, and a decline in biodiversity. It can also have demographic and economic consequences, forcing people to migrate away from affected areas.
Across Europe and other parts of the world, forests are being cleared to make way for greenhouses that produce food on an industrial scale. These greenhouses, while efficient in terms of production, come with a high environmental cost. Unlike forests, which regulate the water cycle, maintain soil health, and support a diverse range of species, greenhouses create an artificial environment devoid of natural elements.
Furthermore, greenhouses require a tremendous amount of energy and resources to operate. They rely on artificial lighting, heating, and irrigation systems, which consume vast amounts of electricity and water. This not only increases the carbon footprint but also drives up the cost of food production. Consumers ultimately bear these costs, with rising prices for fruits, vegetables, and other greenhouse-grown products.

The intensive food industry’s focus on maximizing yield overlooks the long-term sustainability of our environment. The destruction of forests for agricultural expansion is short-sighted, ignoring the invaluable services that natural ecosystems provide. As temperatures rise and biodiversity declines, the impacts of desertification become more pronounced, affecting weather patterns, water availability, and the health of our planet.
To address this crisis, it is crucial to adopt more sustainable farming practices that prioritize environmental conservation. Protecting and restoring forests, integrating agroforestry systems, and reducing reliance on energy-intensive greenhouses are essential steps. By valuing and preserving natural ecosystems, we can mitigate the effects of desertification and ensure a more sustainable and resilient food system for future generations.
In conclusion, the unchecked expansion of the intensive food industry is driving desertification and environmental degradation. The replacement of forests with artificial greenhouses is a major contributor to rising temperatures, declining biodiversity, and increased food costs. It is imperative to rethink our approach to food production and prioritize practices that protect and sustain our natural world.